Plantar fasciitis (Heel Pain)
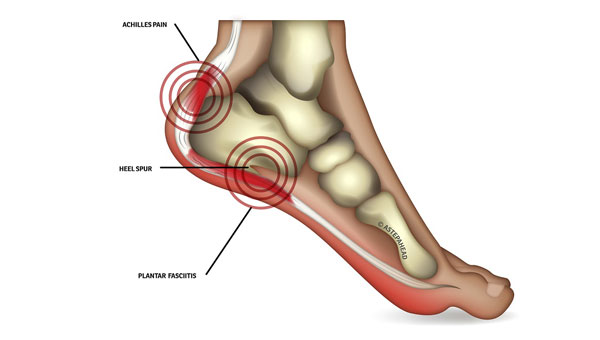
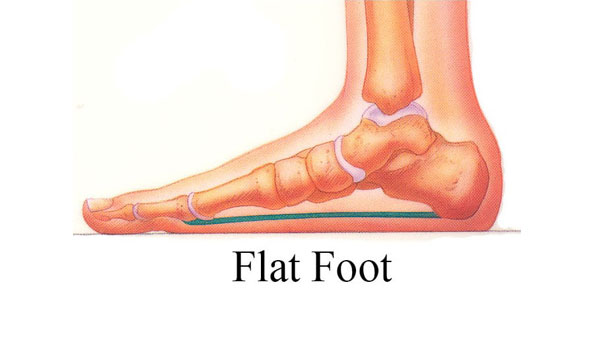
The cause of plantar fasciitis is poorly understood and is thought to likely have several contributing factors.The plantar fascia is a thick fibrous band of connective tissue that originates from themedial tubercle and anterior aspect of the heel bone. From there, the fascia extends along the sole of the foot before inserting at the base of the toes, and supports the arch of the foot.
Originally, plantar fasciitis was believed to be an inflammatory condition of the plantar fascia. However, within the last decade, studies have observed microscopic anatomical changes indicating that plantar fasciitis is actually due to a noninflammatory structural breakdown of the plantar fascia rather than an inflammatory process.
Disruptions in the plantar fascia's normal mechanical movement during standing and walking (known as the Windlass mechanism) are thought to contribute to the development of plantar fasciitis by placing excess strain on the calcaneal tuberosity. Other studies have also suggested that plantar fasciitis is not actually due to inflamed plantar fascia, but may be a tendon injury involving the flexor digitorum brevis muscle located immediately deep to the plantar fascia.